- Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment
-
Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment 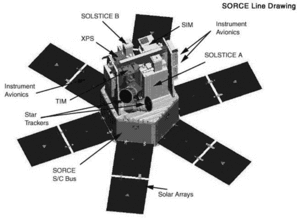
Esquema de SORCE con sus instrumentosOrganización NASA Estado Activo Fecha de lanzamiento 25 de enero de 2003 Vida útil 5-6 años Aplicación Observación solar y terrestre Masa 290 kg Dimensiones Diámetro 1,16 m, longitud 1,6 m Equipo Total Irradiance Monitor (TIM)
XUV Photometer System (XPS)
Solar Stellar Irradiance Comparison Experiment (SOLSTICE)
Spectral Irradiance Monitor (SIM)Elementos orbitales Tipo de órbita Terrestre Inclinación 40 Grados Período orbital 97,31 min Periastro 617 km Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (acrónimo SORCE) es un satélite artificial de la NASA destinado a medir la radiación solar (en el espectro de rayos X, ultravioleta, visible e infrarrojo cercano) que llega a la Tierra para mejorar el conocimiento del clima y mejorar las predicciones climáticas, así como obtener datos sobre el ozono atmosférico. Para realizar las medidas, SORCE utiliza radiómetros, espectrómetros, fotodiodos y bolómetros.
La nave fue construida por Orbital Sciences Corporation y fue lanzada a bordo de un cohete Pegasus XL el 25 de enero de 2003 y está dirigido desde el Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) en la Universidad de Colorado, en Boulder (Colorado).
Contenido
Instrumentos
- Total Irradiance Monitor (TIM)
- Solar Stellar Irradiance Comparison Experiment (SOLSTICE)
- Spectral Irradiance Monitor (SIM)
- XUV Photometer System (XPS)
Especificaciones
- Masa: 290 kg
- Potencia: 348 W
- Comunicaciones: transceptores redundantes en banda S
- Paneles solares: arseniuro de galio
- Longitud: 1,6 m
- Diámetro: 1,16 m
Parámetros orbitales
- Perigeo: 617 km
- Apogeo: 657 km
- Inclinación orbital: 40 grados
- Período: 97,31 min
Referencias
- Wade, Mark (2008). «SORCE» (en inglés). Consultado el 17 de enero de 2009.
Enlaces externos
Categorías:- Observatorios espaciales
- Satélites artificiales lanzados en 2003
- Satélites artificiales de Estados Unidos
Wikimedia foundation. 2010.
